The rise of nationalism in Europe played transformative role in creation of modern nation states. Nationalism arose from two main sources unification of territories with shared cultures as seen in Italy and Germany and resistance against imperial powers governing multi ethnic empires such as Russian and Ottoman Empires. Understanding such theoretical analysis is crucial for UPSC aspirants preparing for mains. APTI PLUS IAS academy in Kolkata helps master these concepts that will help you tackle both prelims as well as mains questions effectively.
Europe in the 19th Century: Fragmented and Diverse
During the 19th century Europe was far from being the continent of nation-states we recognize today. Instead it was a patchwork of fragmented territories, ethnic groups, cultural divisions.
Regions like Germany, Italy, Switzerland were divided into smaller political entities such as kingdoms, duchies, and cantons each with its own ruler. This fragmentation hindered political unity as common cultural or linguistic ties did not necessarily translate into unified governance. Habsburg Empire for example was an extensive and multicultural empire encompassing various regions including Tyrol, Austria, the Sudetenland, Bohemia, Lombardy, Venetia. These areas had different ethnic populations with distinct languages and customs complicating the idea of national identity.
The challenge of political unity especially in the face of linguistic and ethnic diversity was compounded by the existence of autocratic monarchies that prioritized loyalty to the emperor rather than fostering a shared national identity. This created tensions & hindered development of cohesive political unity in many parts of Europe.
Key events and their contributions to the rise of nationalism in Europe
In this regard APTI PLUS top IAS coaching centre in Kolkata provides detailed insights into their features.
-
Napoleon Invades Italy; Napoleonic Wars Begin (1797)
- Napoleon Bonaparte Influence: Napoleonic wars (1803–1815) significantly influenced rise of nationalism across Europe. Napoleon through his conquests spread the ideals of the French Revolution particularly those related to equality, liberty & fraternity across much of Europe.
- Napoleon’s Italian Campaign: In 1797 Napoleon invaded Italy dismantling the old feudal structures and laying the groundwork for the formation of new states. His victory over the Austrian Empire in Italy led to the establishment of the Cisalpine Republic (modern-day Northern Italy) which was essentially a client state of France.
- The Napoleonic Code: Napoleon’s imposition of the Napoleonic Code across his empire further promoted legal equality, the abolition of feudal privileges & rise of a more unified sense of identity, particularly in the regions he controlled.
-
Fall of Napoleon and the Vienna Peace Settlement (1814-1815)
- The Fall of Napoleon: After his defeat in 1814 Napoleon was exiled to the island of Elba and the Congress of Vienna convened to restore European stability. The monarchs and aristocrats aimed to reverse the changes brought about by the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars.
- The Vienna Peace Settlement: In 1815 European powers such as Austria, Russia, Prussia & the United Kingdom met at the Congress of Vienna to redraw the map of Europe. The settlements created balance of power but the dissatisfaction of nationalists and liberals with the conservative order established the foundation for future uprisings.
- Suppression of Nationalism: The Congress aimed to suppress nationalism by reinforcing old monarchies and limiting democratic reforms. However this only served to fuel nationalist sentiments across Europe particularly in countries like Italy, Germany, Poland where nationalist movements began to gain strength.
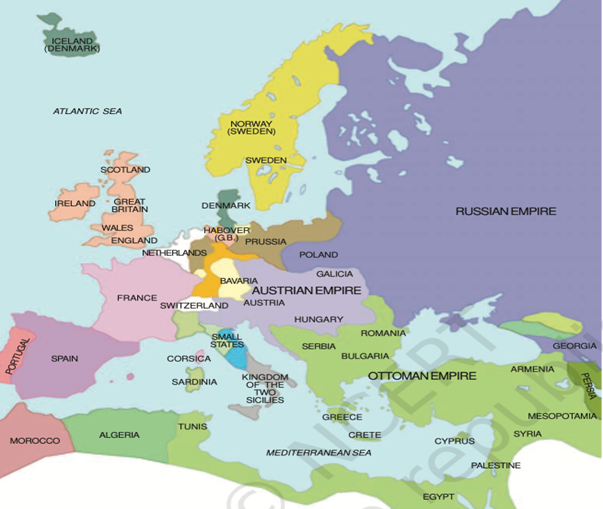
Europe After Vienna Congress
-
The Greek Struggle for Independence (1821)
- Greek War of Independence: Greek struggle for independence from the Ottoman Empire was a key event in the rise of nationalism. In 1821 the Greeks inspired by the ideas of liberty and nationalism revolted against Ottoman rule.
- European Support for Greek Independence: The Greek War of Independence drew support from various European powers including France, Britain, Russia who saw the rebellion as part of a broader European nationalist and anti-imperial movement. In 1827 Battle of Navarino resulted in a decisive victory for the Greek rebels leading to Greece’s independence in 1830.
- Symbol of Nationalism: The Greek revolution inspired other nationalist movements across Europe particularly in the Balkans where many sought to rid themselves of Ottoman control. It was seen as a triumph of national identity and independence.
-
Liberal Revolutions in Europe and the Rise of Nation-States (1848)
- The Revolutions of 1848: Known as the “Springtime of Nations” the revolutions of 1848 were a series of interconnected uprisings across Europe driven by demands for national independence, liberal reforms & constitutional governance.
- Economic Hardships and Revolts: Artisans, industrial workers & peasants who were suffering from economic hardships due to industrialization and poor working conditions played a significant role in these revolutions. They demanded better conditions, higher wages, more political rights.
- Middle Class Demands for Constitutions: Middle class liberals sought constitutional reforms and representative governments. They were heavily influenced by ideas of French Revolution and the desire to create nation states based on democratic principles.
- Nationalism and Revolts in Different Regions:
- Italy: Italians sought to unite the fragmented states of Italy into a single nation state. Nationalist leaders like Giuseppe Mazzini and Giuseppe Garibaldi played key roles in rallying the Italian people.
- Germany: The German Confederation a loose association of German-speaking states experienced revolts with calls for national unification and liberal reforms.
- Hungary: The Hungarian Revolution led by Lajos Kossuth aimed for independence from the Austrian Empire.
- Poland, Czechs, and Slavs: Other regions like Poland, the Czech lands & Slavic-speaking areas demanded self determination and the creation of nation states.
-
Unification of Italy (1859-1870)
- The Italian Unification: The unification of Italy was a major achievement in the rise of nationalism. The Kingdom of Sardinia-Piedmont under the leadership of King Victor Emmanuel II and Prime Minister Count Camillo di Cavour spearheaded the unification movement.
- Garibaldi’s Campaign: The popular leader Giuseppe Garibaldi known for his military prowess played a crucial role in uniting southern Italy with the north. By 1861 the Kingdom of Italy was proclaimed although Rome and Papal States remained outside the unified kingdom until 1870.
- Impact on Nationalism: unification of Italy was significant victory for nationalist movements in Europe showing that unified nation state could be achieved through popular support and military action.
-
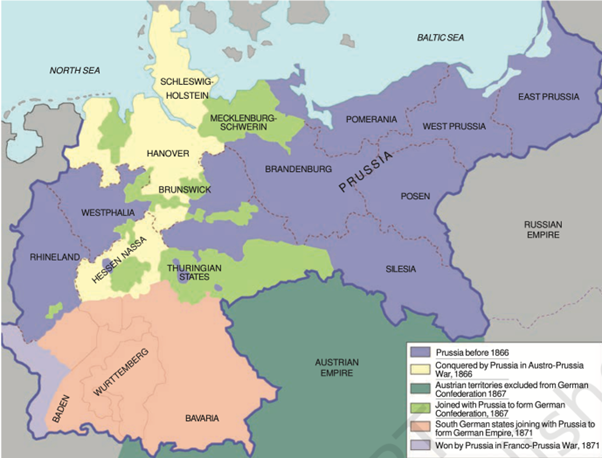
Unification of Germany (1866-1871)
- Otto von Bismarck and German Unification: unification of Germany was primarily driven by the efforts of Otto von Bismarck Prussian prime minister who used both diplomacy and military force to bring together various German states.
- Wars of Unification:
- The Austro-Prussian War (1866): Prussia defeated Austria leading to the dissolution of the German Confederation and the creation of North German Confederation under Prussian leadership.
- The Franco-Prussian War (1870-1871): Bismarck used war against France to unite southern German states with North German Confederation resulting in proclamation of German Empire in 1871.
- Nationalism in Germany: The unification of Germany marked emergence of powerful centralized nation state and rise of German nationalism which had significant implications for European politics.
-
Slav Nationalism in Habsburg and Ottoman Empires (1905)
- Slavic Nationalism: Nationalism among Slavic peoples in the Habsburg and Ottoman Empires grew in the early 20th century. Slavic group including Serbs, Croats, Czechs sought independence or autonomy from the empires that controlled them.
- The Balkan Wars: The decline of the Ottoman Empire in Balkans fueled nationalism. Countries like Serbia, Bulgaria, Greece fought to establish their independence or expand their territories.
- The Role of the Slavic World: pan Slavic movement promoted by figures like Russian Tsar Nicholas II & Serb nationalists sought to unite Slavic peoples against their imperial rulers. This contributed to tensions that led to World War I.
-
World War I (1914-1919)
- The Impact of Nationalism: World War I which lasted from 1914 to 1919 was deeply influenced by the rise of nationalism. The war led to the collapse of several empires including the Austro Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, Russian Empire which created opportunities for nationalist movements to achieve independence.
- The Treaty of Versailles (1919): The post war settlement particularly the Treaty of Versailles resulted in the creation of new nation states in Eastern Europe and Middle East including Poland, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia. These new states were the result of the growing sense of nationalism among their people.
- Nationalism in the Aftermath: Nationalist movements became more prominent in the interwar period leading to the rise of fascism in Italy and Germany as well as the continuation of struggles for self determination in colonial territories.
For more such articles on important topics for UPSC, please visit Resources at APTI PLUS the best coaching institute for IAS Coaching in Bhubaneshwar and Kolkata
Practice Questions
Prelims Questions
- Which of the following was significant impact of French Revolution on Europe?a) Strengthening of absolute monarchies
b) Spread of nationalist ideas
c) Expansion of feudalism
d) Decline of parliamentary institutions
Answer: b) Spread of nationalist ideas
- The unification of Germany in 1871 was largely driven by:
a) Giuseppe Mazzini
b) Giuseppe Garibaldi
c) Otto von Bismarck
d) Napoleon Bonaparte
Answer: c) Otto von Bismarck
- Consider following pairs of wars and their outcomes:
| War | Outcome |
| 1. Franco-Prussian War | Unified Germany under Prussia |
| 2. Austro-Prussian War | Austria took control of German Confederation |
| 3. Crimean War | Strengthened Ottoman Empire |
Which of the pairs are correctly matched?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 1 and 3 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1 only
Answer: b) 1 and 3 only
- Who among following is associated with the “Young Italy” movement?
a) Otto von Bismarck
b) Giuseppe Mazzini
c) Giuseppe Garibaldi
d) Victor Emmanuel II
Answer: b) Giuseppe Mazzini
- Which of following statements regarding Congress of Vienna (1815) is correct?
a) It aimed at restoring pre-revolutionary monarchical regimes in Europe.
b) It supported nationalist movements across Europe.
c) It resulted in the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.
d) It promoted democracy across Europe.
Answer: a) It aimed at restoring pre-revolutionary monarchical regimes in Europe.
Mains Questions
- Discuss role of French Revolution in shaping nationalist movements across Europe.
- Explain significance of Revolutions of 1848 in Europe. Why did most of these revolutions fail?
- Analyze role played by Otto von Bismarck in unification of Germany. How did his policies influence European politics in late 19th century?
- “The unification of Italy was product of both military conquests and diplomatic negotiations.” Discuss.
- Examine impact of nationalism on decline of multinational empires in Europe during 19th and early 20th centuries.
Aspirants must develop a comprehensive understanding of the key developments in Europe in 18th to 20th century essential for answering questions in GS 1, Essay papers. By integrating diverse topics in above practice questions APTI PLUS best test series for UPSC ensures students are UPSC ready with in depth knowledge.





