What are key Concepts in Disaster & Hazard Management?
Disasters whether caused by nature or humans can greatly affect people lives. They can damage homes, roads & buildings & sometimes lead to loss of life & jobs. To prepare for & reduce damage caused by disasters it is important to understand different types of disasters & hazards. This article will explain types of disasters, what causes them & how they impact our lives in a simple way.
APTI PLUS UPSC Coaching provides comprehensive study materials & expert guidance to help IAS aspirants master disaster management topics making sure strong conceptual understanding for exam.
Before we learn about different types of disasters we need to understand some important ideas that help us manage & reduce their effects.
Disaster is a sudden & serious event that causes big problems for people & their surroundings. It can damage homes, roads & nature making it difficult for people to recover without outside help.
Hazard is anything that can cause harm. It can come from nature like earthquakes, floods or storms or from human activities like factory accidents, pollution or terrorist attacks.
Vulnerability means how easily a place or group of people can be affected by a disaster. If people are poor, have weak buildings or are not prepared for emergencies they are more vulnerable to disasters.
Risk is chance of a disaster happening & how much damage it might cause. It depends on how often hazards occur & how vulnerable people are. Risk includes things like loss of life, injuries, damage to buildings & harm to nature.
Capacity is how well people & communities can prevent, deal with & recover from disasters. Good capacity means having trained people, strong buildings, enough money & good plan to handle disasters.
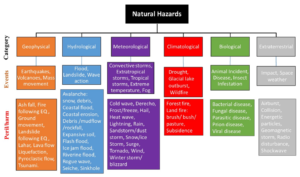
Classification of Disasters
Disasters can be classified based on their causes, scale, duration & impacts. The two primary categories of disasters are natural disasters & human made disasters.
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters are caused by environmental forces & geological, hydrological, meteorological, climatological & biological processes.
Geophysical Disasters (Earth Processes & Movements)
Geophysical disasters happen because of natural movements & changes inside Earth. These disasters can cause serious damage to land, buildings & people lives.
Earthquakes happen when ground suddenly shakes due to movement of large pieces of Earth surface (tectonic plates). They can cause buildings to fall, landslides & giant ocean waves called tsunamis.
Volcanic Eruptions happens when a volcano releases hot lava, ash & gases. This can destroy nearby areas, pollute air & even affect weather.
Tsunamis are huge ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes, landslides or volcanic eruptions. They can flood coastal areas, destroy buildings & take many lives.
Landslides occur when rocks, soil or debris slide down a hill or mountain. They often happen because of earthquakes, heavy rain or when trees are removed from slopes.
Avalanches are when a large amount of snow & ice suddenly rushes down a mountain. They usually happen in snowy areas due to earthquakes, storms or even human activity.
With its structured test series & answer writing practice APTI PLUS top IAS Coaching Centre in Kolkata enables aspirants to effectively tackle disaster related questions in Prelims, Mains & Interviews.
Meteorological Disasters (Weather & Atmospheric Conditions)
These disasters result from atmospheric processes & extreme weather conditions.
Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes, Typhoons) Powerful rotating storms formed over warm ocean waters bringing strong winds, heavy rainfall & storm surges.
Thunderstorms & Lightning Storms characterized by thunder, lightning, heavy rainfall & strong winds. Lightning strikes can cause wildfires, fatalities & infrastructure damage.
Tornadoes Violently rotating columns of air extending from a thunderstorm to ground causing destruction along their paths.
Extreme Temperatures Prolonged periods of unusually hot (heatwaves) or cold (cold waves) weather posing health risks & economic consequences.
Hydrological Disasters (Water Related Events)
These disasters involve movement & distribution of water.
Floods Overflow of water onto normally dry land due to heavy rainfall, river overflow, dam failures or storm surges.
Flash Floods Sudden, localized floods caused by intense rainfall particularly in urban areas with poor drainage.
Landslides Although primarily geological, landslides are often triggered by water saturation from heavy rains.
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) Sudden discharge of water from glacial lakes causing downstream flooding.
Climatological Disasters (Long Term Climate Variability)
These disasters result from long-term weather patterns & environmental changes.
Droughts Extended periods of below-average rainfall leading to water shortages, crop failure & food insecurity.
Wildfires Uncontrolled fires in forests or grasslands often triggered by high temperatures, dry conditions & human activity.
Heatwaves & Cold Waves Prolonged periods of excessive heat or cold causing health hazards, power shortages & environmental stress.
Biological Disasters (Living Organisms & Disease Outbreaks)
Biological disasters arise from disease outbreaks & interactions between organisms & environment.
Epidemics & Pandemics Rapid spread of infectious diseases (for example COVID-19, Ebola, influenza) affecting human populations.
Insect Infestations Large swarms of pests such as locusts damaging crops & leading to food shortages.
Animal Stampedes Sudden, uncontrolled movement of animals often triggered by environmental stressors or human activities.
Human Made Disasters
These disasters result from human activities, technological failures, industrial processes & socio political conflicts.
Industrial & Technological Disasters
Chemical Spills Accidental leakage of hazardous substances into environment causing pollution & health risks.
Nuclear Accidents Radiation leaks from power plants or nuclear weapon testing leading to long term environmental & health consequences (for example Chernobyl, Fukushima).
Infrastructure Failures collapse of bridges, buildings & transportation systems due to poor construction, maintenance failures or external impacts.
Environmental Disasters
Deforestation Large scale clearing of forests leading to biodiversity loss, soil erosion & climate change.
Pollution (Air, Water & Soil) Contamination of natural resources by industrial waste, chemicals & plastic.
Climate Change Driven Disasters Increased frequency of extreme weather events due to global warming & environmental degradation.
Social & Political Disasters
Wars & Conflicts Armed conflicts leading to mass displacement, economic decline & infrastructure destruction.
Terrorism Violent attacks aimed at causing fear & disruption often targeting civilians & critical infrastructure.
Civil Unrest Large scale protests, riots or government instability affecting public order & security.
Disasters in India
Indian diverse geography & climatic conditions make it highly susceptible to multiple types of disasters.
Floods Every year, heavy rains during monsoon season cause floods in many areas. States like Bihar, Assam & Uttar Pradesh are badly affected & millions of people suffer.
Cyclones Powerful storms called cyclones often hit eastern & western coasts of India. They bring strong winds, heavy rain & floods damaging homes as well as farms in coastal areas.
Earthquakes Himalayan region is at high risk of earthquakes. When ground shakes, buildings can collapse & landslides can happen causing serious damage.
Droughts Some places like Rajasthan & Gujarat do not get enough rain. This leads to droughts which means there is little water for drinking & farming.
Heatwaves Northern & central India often experience extremely high temperatures in summer. These heatwaves can make people sick & in some cases even cause deaths.
Forest Fires In states like Uttarakhand & Himachal Pradesh large fires can break out in forests, destroying trees, harming animals & polluting air.
Tsunamis Indian coastline is at risk of tsunamis which are huge sea waves caused by underwater earthquakes. 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami caused massive destruction & loss of life.
APTI PLUS best coaching for UPSC offers specialized mentorship & interactive sessions on contemporary issues like climate change, pandemics & industrial hazards keeping aspirants updated with relevant case studies.
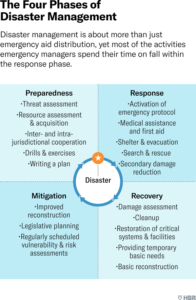
Disaster Management Cycle
Disaster management is a continuous process that helps us prepare for disasters, reduce their impact & recover from them. It has four main stages
Mitigation (Prevention) means taking steps to reduce the risk of disasters. Governments & communities can do this by making strong rules for building houses, planning land use wisely, and improving infrastructure like roads & bridges.
Preparedness means getting ready before a disaster happens. It includes setting up early warning systems, practicing safety drills & making sure people know what to do in an emergency.
Response This is what happens right after a disaster. The goal is to save lives & help people who are affected. This includes rescue operations, providing food, water & medical help & making sure everyone is safe.
Recovery is process of rebuilding after a disaster. It includes repairing homes, roads & schools as well as making communities stronger so they can handle future disasters better.
Conclusion
A deep understanding of disaster classification is important for risk assessment, disaster preparedness & resilience building. By identifying hazards, reducing vulnerabilities & strengthening disaster management frameworks societies can minimize losses & increase their ability to recover from catastrophic events.
By integrating disaster management topics into its current affairs modules APTI PLUS IAS Coaching in Kolkata makes sure that IAS aspirants develop analytical skills to link theoretical concepts with real world applications.
Practice Questions
Prelims Questions
- Which of following is NOT classified as geophysical disaster?
a) Earthquake
b) Tsunami
c) Flood
d) Volcanic eruption
Answer (c)
- Consider following statements regarding biological hazards
- Epidemics & pandemics are both forms of biological disasters.
- Insect infestations can impact food security & public health.
- Biological disasters are always natural & cannot be human induced.
Which of above statements are correct?
a) 1 & 2 only
b) 2 & 3 only
c) 1 & 3 only
d) 1, 2 & 3
Answer (a)
Mains Questions
- What are major classifications of disasters? Discuss how vulnerability & capacity influence disaster risk in India.
- India is highly prone to hydrological & meteorological hazards. Examine role of disaster preparedness & mitigation strategies in reducing their impact.



