What is Cyber Security & Cyberspace?
As per the Information Technology Act, 2000: Cybersecurity refers to protection of information, devices, computer systems, communication devices & stored data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification or destruction.
As per the India Cyber Security Policy, 2013: Cyberspace is complex environment where people, software & services interact supported by global distribution of information & communication technology devices & networks. It is global domain that encompasses an interdependent network of IT infrastructures including internet, telecommunication networks, computer systems & embedded processors.
APTI PLUS IAS Coaching in Kolkata equips IAS aspirants empowering them to tackle complex subjects like cybersecurity effectively & excel in dynamic & evolving civil services exam.
What are major Cyber threats?
Cyber Crime/Cyber Attacks
An offensive maneuver targeting computer systems, networks or infrastructures with intention to damage, disrupt or destroy them.
These attacks may range from spyware installation to large scale attacks aiming to destroy national infrastructure. Depending on the scale and impact cyber attacks may be classified as: Cyber Campaigns, Cyber Warfare, Cyber Terrorism

Cyber Espionage involves using computer networks to illicitly access confidential data typically from governments or large organizations. It often focuses on intelligence gathering or data theft but may also involve analyzing public activities on social platforms.
Notable examples include: Titan Rain, Moonlight Maze etc.
Cyber Terrorism refers to unlawful attacks or threats against computer networks & information systems often to intimidate or coerce governments or their citizens. While it can cause physical damage it can also be a non violent form of terrorism if it generates fear or disrupts critical infrastructure.
Beyond attacking systems cyber terrorists also use cyberspace for planning, communication, recruitment, propaganda & financing. These acts may aim to further political or social agendas through digital means.
Cyber Warfare is use of computer technologies by states or organizations to disrupt or destroy activities of other nations or entities. This may include stealing sensitive information or disrupting critical systems. Attacks may be covert (to extract information without disturbing operations) or overt (aimed at causing damage or disruption).
Key Cyber Players
| Type of Cyber Actor | Motive | Example Activities |
| Cyber Criminals | Financial gain through hacking banks, phishing scams and ransomware attacks. | ● Hacking bank accounts
● Phishing scams ● Ransomware attacks |
| Cyber Terrorists | Attacking national infrastructure to further political objectives or exert political power. | ● Attacks on critical infrastructure
● Disrupting national services to spread political messages |
| Cyber Espionage Actors | Gathering intelligence and stealing sensitive data from corporate and military systems. | ● Stealing corporate trade secrets
● Military data breaches ● State-sponsored hacking |
| Cyber Hacktivists | Using hacking techniques to promote political agendas often through disruptive online actions. | ● Attacks on government websites
● Campaigns for social/political change ● Spreading viral messages (e.g., Anonymous) |
| Cyber Vandals | Destruction and disruption of systems without a specific financial or political motive often for thrill. | ● Defacing websites
● Launching Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks for fun or as a prank |
| Insider Threats | Individuals within an organization exploiting access to steal data, sabotage systems or harm the company. | ● Data theft
● Sabotaging internal systems ● Leaking sensitive information to external actors |
| Script Kiddies | Inexperienced hackers using pre-written tools or scripts to exploit vulnerabilities often for personal gain or thrill. | ● Executing automated attacks using available tools
● Hacking for fun or personal recognition |
| State Sponsored Actors | Engaging in cyber activities on behalf of a government to achieve strategic, military or geopolitical goals. | ● Cyber warfare
● Stealing sensitive government or corporate data ● Disrupting foreign elections or infrastructure |
| Cyber Merchants | Profit-driven actors who engage in selling or trading stolen data, malware and hacking tools. | ● Selling personal data
● Running black-market websites for malware and hacking tools |
| Cyber Activists | Advocating for social, environmental, or political change through cyber means often non-violent. | ● Attacking corporations or government agencies for policy protests
● Exposing corruption or human rights abuses |
| Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) | Highly skilled and sophisticated cyber actors, typically state-sponsored focusing on long-term espionage. | ● Persistent data theft over a prolonged period
● Compromising high-value targets like government or defense contractors |
| Cyber Blackmailers | Extorting victims by threatening to release sensitive or embarrassing information unless a ransom is paid. | ● Data breaches with the threat of public exposure
● Threatening to release sensitive or compromising personal data |
Importance of Cyberspace
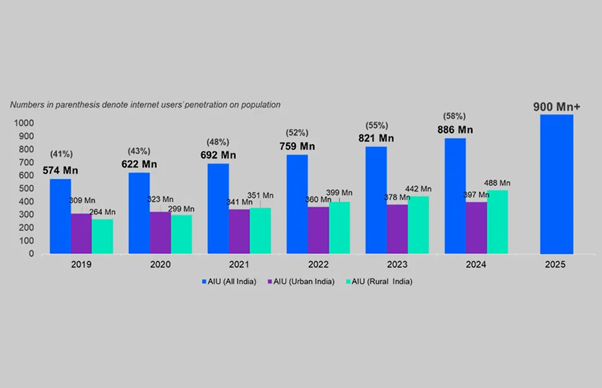
State of India’s Digital Economy
| Category | Data (2025) | Additional Insights |
| Total Internet Users | ~900 million users | India is one of the largest internet populations globally. |
| Internet User Growth (CAGR) | ~10% CAGR over the past 5 years | Reflects rapid adoption of digital technologies. |
| Transacting Users | ~250 million online shoppers, ~200 million digital payment users | E-commerce and digital payments are booming, with digital India initiatives driving adoption. |
| Gaming Users | ~500 million gamers (expected by 2025) | India’s gaming market is one of the largest globally, fueled by mobile gaming growth. |
| Online Gaming Market Value | ₹23,000 crore (~US$2.8 billion) in 2023, expected to reach ₹70,000 crore (~US$8.6 billion) by 2027 | Online gaming is expanding rapidly with a diverse market of mobile and fantasy sports platforms. |
| Top Gaming Players | – Dream11: 130 million users – MPL (Mobile Premier League): 99 million users – Nazara Technologies, Games24x7 |
These platforms lead the online gaming industry in India. |
| Average Daily Screen Time | 4–5 hours | Includes activities such as social media, video streaming, gaming, and browsing. |
| Mobile Gaming Share | Dominates the market | Affordable smartphones and 4G internet have made mobile gaming accessible to millions of users. |
| E-commerce Growth | Expanding rapidly, driven by increased internet penetration | The e-commerce sector is seeing a surge in user base with more people buying online due to convenience. |
| Digital Payment Users | ~200 million active digital payment users | UPI (Unified Payments Interface) adoption is accelerating, with many using mobile wallets for daily transactions. |
| Smartphone Penetration | ~90% of internet users access the internet via smartphones | Smartphones are the primary device for internet access, further driving digital engagement. |
| Internet Penetration in Rural Areas | 55–60% (growing steadily) | Internet penetration is expanding rapidly in rural India, thanks to affordable smartphones and initiatives like BharatNet. |
| Average Internet Speed | 14.2 Mbps (global ranking 73rd, but improving with 5G rollout) | The introduction of 5G networks is expected to improve internet speeds significantly across urban and rural India. |
APTI PLUS UPSC Coaching in Bhubaneshwar provides comprehensive guidance & strategic insights helping IAS aspirants navigate complex topics like cybersecurity ensuring they are well prepared for evolving demands of civil services exam.
Cost of Internet in India
| Category | Data Cost (2025) | Additional Insights |
| Cost of Data | ₹10 to ₹15 (~US$0.12 to US$0.18) per GB for average data, ₹250 to ₹400 (~US$3 to US$5) for 1GB/day plans | India has some of the lowest data costs globally, driven by intense telecom competition and government support. |
Cybercrime in India
Cybercrime Statistics (Based on NCRB and FBI Reports)
| Year | Cybercrime Increase | Cybercrime Cases | Main Motives | Top Cybercrimes by Motive |
| 2022 | 24% increase in cybercrimes from 2021 | 65,893 cases | Fraud (64.8%), Extortion (5.5%), Sexual Exploitation (5.2%) | Fraud (42,710), Extortion (3,648), Sexual Exploitation (3,434) |
| 2021 | India ranks 3rd among top 20 victim countries of internet crimes | – | – | – |
| Q1 2024 | 33% year-on-year increase in attacks | 2,807 attacks/week | – | – |
Examples of Cyber-Attacks in India
| Year | Cyber Attack Description |
| 2012 | Email accounts of 12,000 people, including officials from Ministry of External Affairs, Ministry of Home Affairs, DRDO, ITBP breached. |
| 2013 | NPCIL faced up to 10 targeted attacks per day, blocking them. |
| 2016 | 32 lakh debit cards compromised. |
| 2017 | Legion group hacks emails and twitter accounts, claims access to over 40,000 servers, encryption keys, medical data from private hospitals. |
| 2017 | Petya Ransomware attack impacts container handling at Mumbai’s Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust. |
| 2017 | WannaCry ransomware attack locks thousands of computers, impacts Andhra Pradesh Police and West Bengal state utilities. |
Strategic Importance of Cyberspace
- Public Policy & Governance
Cyberspace plays crucial role in execution of public policies like Digital India initiative & payment infrastructures such as UPI. It also stores & processes sensitive governmental data & any breach could have severe consequences on national security & public services. - Critical Infrastructure
Many essential services including railways, defense systems, communications, banking, financial systems rely on cyberspace. A disruption in cyberspace could cripple these services affecting daily life & national security. - National Security
States are developing capabilities to engage in cyberattacks that can influence or alter outcomes on battlefield making cyberspace component of national defense strategies. - Vulnerabilities of Users
With growing number of online transactions & internet-based services users have become increasingly vulnerable to cybercrimes including online banking frauds, surveillance, profiling, privacy violations.
Challenges in Cyber Space Domain
- Diffuse & Intangible Threats
The anonymity & low cost of attacks make it difficult to identify perpetrators & launch strong, timely response. Attackers can operate without physical constraints & mislead target into thinking the attack originated from elsewhere. - Global Nature of Cyberspace
Cyberspace is inherently international & protecting national interests requires global cooperation. Cyber threats may arise anywhere in the world impacting the security of nation digital infrastructure. - Technological Advancements
Rapidly evolving technology requires constant investment, manpower & ecosystem to track global developments, develop countermeasures & stay ahead of emerging threats. - Vulnerable Systems
The absence of foolproof security & low costs for attackers to launch cyberattacks mean that even minor flaws in system can lead to significant breaches. - Human Element in Cybersecurity
Many cyberattacks involve human error such as users falling for phishing scams or compromising sensitive information unknowingly.
| Attack Type | Targets | Effects | Mitigation Challenges |
| Insider Attack | Human, Organization | Disinformation, Distraction, Confusion | ● Monitoring insider behavior
● Access control and user verification |
| Unwitting Behaviour | Human, Organization | Data and Policy Corruption | ● Employee training
● Robust anti-phishing measures |
| Space Mission Layer | Command & Control Systems | Disruption, Behavioral Manipulation | ● Secure communication protocols
● Redundancy in critical systems |
| Software Layer | Applications, OS, Network | Induced Inaccuracies, Failures, Denial of Service | ● Regular software updates
● Vulnerability patching |
| Hardware Systems Layer | Hardware, Physical Devices | Malfunction, Performance Loss, Physical Destruction | ● Stronger hardware encryption
● Monitoring hardware integrity |
| Materials, Devices & Communication Links | Communication Systems | Loss of Communication | ● Secure data transmission channels
● Backup communication systems |
Mitigation Challenges
| Mitigation Measure | Explanation |
| Development Environment Access Control | Prevent unauthorized access during software development ensuring system integrity. |
| Architectural Considerations | Embed cybersecurity within system architecture minimizing potential vulnerabilities. |
| Technology and Tools | Use advanced cybersecurity tools (e.g., firewalls, intrusion detection) to detect and respond to threats. |
| Informed Operator Responsiveness | Ensure operators are trained and equipped to quickly identify and respond to cyber threats. |
Government Steps in Cybersecurity
Legal Framework
| Framework/Act | Key Provisions |
| National Cybersecurity Strategy 2020 | Focus on 21 areas for a resilient cyberspace: large-scale digitization security, supply chain security, digital payments security, and more. |
| National Cybersecurity Policy 2013 | Establishes NCIIPC, aims to create 5,00,000 cybersecurity professionals in 5 years, and offers fiscal schemes for cybersecurity adoption. |
| Information Technology Act 2000 | Regulates the use of computer systems, networks, electronic contracts, cybercrimes, and more. Addresses hacking, cyber terrorism, and data protection. |
| Key Limitations | Issues with corporate data protection, small compensation limits (Rs. 5 crore) and inadequate spam management. |
Criminal Offenses under Information Technology Act, 2000
| Criminal Offense | Section of IT Act | Details |
| Hacking | Section 66 | Hacking a computer system or network, unauthorized access, and data alteration. |
| Cyber Terrorism | Section 66F | Accessing a protected system with the intent to threaten the unity, integrity, sovereignty, or security of India. |
| Cheating using computer resources | Section 66C | Using a computer resource or communication device to cheat or defraud. |
| Tampering with computer source documents | Section 65 | Altering, destroying, or concealing any document or data stored in a computer system. |
| Identity Theft | Section 66C | Using someone else’s identity to gain unauthorized access or commit fraud. |
| Cyberstalking | Section 66A (now repealed) | Sending offensive or threatening messages through computer systems. |
| Obscenity and Pornography | Section 67 | Publishing, transmitting, or creating obscene content via electronic means. |
| Publishing defamatory content | Section 66A (now repealed) | Sending offensive or defamatory messages online or through digital means. |
| Sending offensive messages through communication service | Section 66A (now repealed) | Sending offensive, menacing, or false information with the intent to cause harm. |
| Cyber Squatting | Section 66A (now repealed) | Registering a domain name with the intent to sell it later at an inflated price. |
| Data Theft and Privacy Violations | Section 72 | Disclosure or sharing of personal data or information in breach of a lawful contract or without consent. |
| Misuse of Digital Signature | Section 73 | Using a digital signature to commit fraud or unauthorized actions. |
| Access to protected systems | Section 70 | Accessing critical infrastructure and sensitive systems without authorization. |
Institutional Framework:
| Institution/Initiative | Details |
| NCIIPC | 24×7 National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre for securing critical infrastructure. |
| CERT-In | National nodal agency for coordinating cybersecurity with local CERTs for state level coordination. |
| Cybersecurity Task Force | Aiming to train 5 lakh cybersecurity professionals in 5 years. |
Other Government Measures:
| Area of Focus | Key Measures |
| Digital Payments Security | Threat modelling, vulnerability disclosure, and intelligence sharing to secure digital payment systems. |
| State-Level Cybersecurity | Development of state cybersecurity policies, allocation of funds, and guidelines for security architecture. |
| SME Cybersecurity | Incentives for SMEs adopting cybersecurity standards and IoT security frameworks. |
| Cyber-insurance | Development of cyber-insurance products to mitigate financial risks from cyber threats. |
Key Challenges in Cybersecurity
- Cybercrime Growth: With increase in cybercrime rates especially fraud & extortion challenge lies in both preventing & responding to these attacks.
- Inadequate Implementation of Policies: National Cybersecurity Policy 2013 has faced challenges in implementation particularly regarding recruitment of cybersecurity professionals & balancing privacy with cybersecurity.
- Protection of Critical Infrastructure: Protecting critical information infrastructure from cyber-attacks requires integrating cybersecurity measures within all digitized services & monitoring critical sectors like energy, defense, healthcare.
- Lack of Comprehensive Spam Laws: While other countries have strict anti-spam laws India laws have not adequately addressed this growing issue which hampers effective prevention of spam & data breaches.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is critical aspect of our increasingly digital world requiring robust measures to protect sensitive data, systems & infrastructures from various threats. APTI PLUS Best Coaching for UPSC through such insights tries to apprise IAS aspirants on its importance & prepare for UPSC exam.
For further insights, we will discuss global cybersecurity strategies & best practices in Part 2.